
Understanding TCP/IP is essential for anyone working in IT or networking. It’s a fundamental part of how the internet and most networks operate. Whether you’re just starting or you’re looking to move up in your career, knowing TCP/IP inside and out can really give you an edge.
In this blog post, we’re going to go through the top 50 TCP/IP interview questions and answers. We’ve included questions for all levels, from beginners to advanced, so you can be prepared no matter where you are in your career. These questions will help you get a solid grasp of the basics, understand the deeper mechanics, and see how TCP/IP works in real-world situations. Let’s dive in and get you ready to ace that interview!


The private IP address of a system is the IP address that is used to communicate within the same network. Using private IP data, information can be sent or received within the same network. For more details please refer difference between private and public IP addresses.
IP itself doesn’t guarantee delivering data correctly. It leaves all data protection to the transport protocol. Both TCP and UDP have mechanisms that guarantee that the data they deliver to an application is correct.
Using the IP layer, the correct destination of the packet is identified & delivered. The Transport layer protocols(TCP/UDP) check if the data delivered is correct using the Checksum mechanism. However, if the destination IP is not alive, the packet is hopped by decreasing the TTL (Time to leave) field and when it becomes zero, the packet is lost and undelivered. If the transport layer is UDP, the source doesn’t know of the failure in the delivery of the packet. For more details please refer IP address
The protocol data unit of the transport layer is a segment or datagram.
5. Tell the name of the data unit to send by the Internet layer?
The protocol data unit of the internet layer is a packet.
| Transmission control protocol (TCP) | User datagram protocol (UDP) |
|---|---|
| TCP is a connection-oriented protocol. Connection-orientation means that the communicating devices should establish a connection before transmitting data and should close the connection after transmitting the data. | UDP is the datagram oriented protocol. This is because there is no overhead for opening a connection, maintaining a connection, and terminating a connection. UDP is efficient for broadcast and multicast types in order of network transmission. |
| TCP is reliable as it guarantees the delivery of data to the destination router. | The delivery of data to the destination cannot be guaranteed in UDP. |
| TCP provides extensive error checking mechanisms. It is because it provides flow control and acknowledgement of data. | UDP has only the basic error checking mechanism using checksums. |
| Sequencing of data is a feature of Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). This means that packets arrive in-order at the receiver. | There is no sequencing of data in UDP. If the order is required, it has to be managed by the application layer. |
| TCP is comparatively slower than UDP. | UDP is faster, simpler, and more efficient than TCP. |
| Retransmission of lost packets is possible in TCP, but not in UDP. | There is no retransmission of lost packets in the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). |
| TCP has a (20-60) bytes variable length header. | UDP has an 8 bytes fixed-length header. |
| TCP is heavy-weight. | UDP is lightweight. |
| TCP doesn’t support Broadcasting. | UDP supports Broadcasting. |
| TCP is used by HTTP, HTTPs, FTP, SMTP and Telnet. | UDP is used by DNS, DHCP, TFTP, SNMP, RIP, and VoIP. |
For more details please refer difference between TCP and UDP article.
TCP is reliable as it uses checksum for error detection, attempts to recover lost or corrupted packets by re-transmission, acknowledgment policy, and timers. It uses features like byte numbers and sequence numbers and acknowledgment numbers so as to ensure reliability.
For more details please refer TCP/IP in the computer networking article.

For more details, please read TCP/IP model article.
A TCP Flag field contains 6 different flags, namely:
For more details, please read TCP/IP model article.
One of the important fields of TCP protocol format. It is 16 bits long. This field holds the checksum for error control. It is mandatory in TCP as opposed to UDP. For more details, please read TCP/IP model article.
A port is basically a physical docking point that is basically used to connect the external devices to the computer, or we can say that a port acts as an interface between the computer and the external devices, e.g., we can connect hard drives and printers to the computer with the help of ports. For more details please refer to various TCP and UDP ports article.
13.Write the name of the Well-Known Port used by TCP?
| PORT | Service | Description | Transport Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | Echo | Port just echoes whatever is sent to it. This feature can be used in many attacks, such as Smurf/Fraggle. | TCP and UDP |
| 9 | Discard | Discard any datagram that is received. | |
| 20 /21 | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) | Port used by FTP protocol to send data to a client. | TCP |
| 23 | Telnet | Port used by Telnet to remotely connect to a workstation or server(unsecured) | TCP |
| 25 | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | Used to send E-Mail over the Internet | TCP |
| 53 | Domain Name System (DNS) | Port for DNS requests, network routing, and zone transfers | TCP |
| 67 | BOOTP | Bootstrap protocol | TCP |
| 80 | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) | Used for browsing web-pages on a browser | TCP |
| 110 | Post Office Protocol (POP3) | Port used to retrieve complete contents of a server mailbox | TCP |
For more details please refer to various TCP and UDP ports article.
TcpEndpoint allows you to easily establish and communicate over TCP/IP network connections between client and server processes, possibly residing on different hosts. The TcpEndpoint class follows a telephone-like model of networking: clients “call” servers and servers “answer” clients. Once a network connection is established between a client and a server, the two can “talk” to each other by reading from and writing to the connection.
TCP protocol has methods for finding out corrupted segments, missing segments, out-of-order segments, and duplicated segments.
Error control in TCP is mainly done through the use of three simple techniques :
A state occurring in the network layer when the message traffic is so heavy that it slows down network response time is known as congestion. For more details please read TCP congestion control article.
17.What is the difference between stop-and-wait protocol & sliding window protocol?
Efficiency of Stop-and-Wait Protocol is
Efficiency of sliding window protocol is
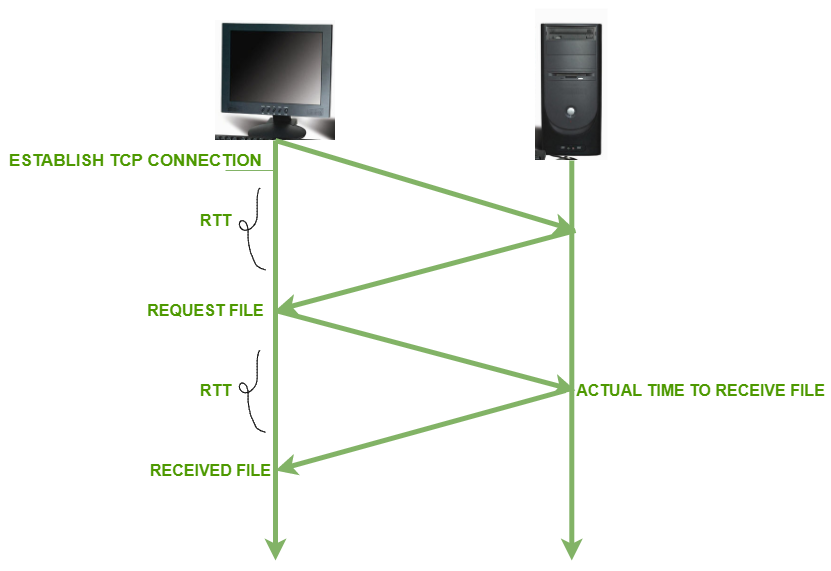
The length of time taken by a data packet to be sent to a destination includes the time it takes for an acknowledgment of that packet to be received back at the original place. For more details please refer to What is RTT article.
TCP acknowledgments are used to acknowledge packets that are successfully received by the host. The flag is set if the acknowledgment number field contains a valid acknowledgment number.For more details, please read TCP/IP model article.
20.What is retransmission?
The TCP retransmission means resending the packets over the network that have been either lost or damaged. Here, retransmission is a mechanism used by protocols such as TCP to provide reliable communication. Here, reliable communication means that the protocol guarantees the packet’s delivery even if the data packet has been lost or damaged. The networks are unreliable and do not guarantee the delay or the retransmission of the lost or damaged packets. The network, which uses a combination of acknowledgment and retransmission of damaged or lost packets, offers reliability. For more details please read TCP congestion control article.
21.If TCP round trip time, RTT is currently 30m sec and the following acknowledgment comes in after 26, 32 and 24 m sec respectively what is the new RTT estimate?(Use α = 0.9)
The formula for estimate new RTT
[Tex]new RTT = α RTT+(1-α )arrival RTT[/Tex]
new RTT = 0.9*30+(1-0.9)*26
For more detail please refer what is RTT article.
For more details, please read TCP/IP model article.
SCTP stands for Stream Control Transmission Protocol . It is a connection-oriented protocol on computer networks that provides a full-duplex association, i.e., transmitting multiple streams of data between two endpoints at the same time that have established a connection in the network. It is sometimes referred to as next-generation TCP or TCPng. SCTP makes it easier to support telephonic conversation on the Internet. A telephonic conversation requires the transmitting of the voice along with other data at the same time on both ends. The SCTP protocol makes it easier to establish a reliable connection.SCTP is also intended to make it easier to establish connections over the wireless networks and managing the transmission of multimedia data. SCTP is a standard protocol (RFC 2960) and is developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). For more details please read the SCTP full form article.
Process of three-way handshaking protocol
Steps 1, 2 establish the connection parameter (sequence number) for one direction and it is acknowledged. Steps 2, 3 establish the connection parameter (sequence number) for the other direction and it is acknowledged. With these, full-duplex communication is established.
For more details please read TCP-3 way handshake process.
| Leaky Bucket | Token Bucket |
|---|---|
| When the host has to send a packet, the packet is thrown in a bucket. | This leaky bucket holds tokens generated at regular intervals of time. |
| Bucket leaks at a constant rate | The bucket has a maximum capacity. |
| Bursty traffic is converted into uniform traffic by leaky buckets. | Bucket there is a ready packet, a token is removed from the bucket and the packet is sent. |
| In practice, a bucket is a finite queue output at a finite rate. | If there is no token in the bucket, the packet can not be sent. |
| S.NO | Connection-oriented Service | Connection-less Service |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Connection-oriented service is related to the telephone system. | Connection-less service is related to the postal system. |
| 2. | Connection-oriented service is preferred by long and steady communication. | Connection-less Service is preferred by bursty communication. |
| 3. | Connection-oriented Service is necessary. | Connection-less Service is not compulsory. |
| 4. | Connection-oriented Service is feasible. | Connection-less Service is not feasible. |
| 5. | In connection-oriented Service, Congestion is not possible. | In connection-less Service, Congestion is possible. |
| 6. | Connection-oriented Service gives the guarantee of reliability. | Connection-less Service does not give the guarantee of reliability. |
| 7. | In connection-oriented Service, Packets follow the same route. | In connection-less Service, Packets do not follow the same route. |
| 8. | Connection-oriented services require a bandwidth of a high range. | Connection-less Service requires a bandwidth of low range |
In TCP, connection-oriented transmission requires three phases:
For more detail read TCP connection establishment article.
Features of the TCP sliding window:
Port addressing is done by the transport layer, which is the 4th layer of the OSI (Open System Interconnection) Model. Port addresses are short because they have to perform the end-to-end delivery of the message and the protocols are less in number than computer systems, therefore, port addresses are less than IP addresses. The IP address refers to the computer/device connected to the network and the port address refers to a particular protocol to communicate with the server as per client request. For more details read TCP/IP ports and its application article.
No, UDP is unreliable and connectionless. While IP unreliability lies in the upper layer protocols. The IP packet becomes reliable if the upper layer protocol is TCP. In terms of data integrity, UDP is more reliable than IP. The checksum in the IP header only applies to the header itself, not to the whole packet. The UDP checksum applies to the whole user segment.
It is a logical unit to transfer information over the network. This data is transmitted from source to destination. It does not guarantee that data will be delivered or lost on the way. It has two section headers and a data payload. It travels in-network without establishing a prior virtual network between source and destination., ie. unlike, it has no prior information about the path between source and destination. This data is frequently divided into smaller parts and transmitted to the defined route.
Registered port: The ports ranging from 1024 to 49151 are not assigned and controlled by an IANA. They can only be registered with IANA to prevent duplication.
Dynamic port: This port ranging from 49152 to 65535 is neither controlled nor registered. They can be used in any process.
The lifespan or lifetime of data that is being sent. Once, after that specified time is over or elapsed, the data will be discarded or it can also be stated as a number of hops that packet is set to exist in the network, after which that packet is discarded. The purpose of the TTL field is to avoid a situation in which an undeliverable datagram keeps circulating in the network.
An IPv4 packet has arrived with the first 8 bits being 01000010 The receiver discards the packet because the first 4 bits represent version IPV4.
and another 4 bits represent header length (/ 4) which should range between 20 to 60 bytes. Here 0010 represents header length, is equal to 2 * 4 = 8. So, the receiver will reject the packet.
If an IPv4 packet, the value of HLEN is 1000 in binary, then 32 bytes of options are carried by this packet.
Open-loop congestion control policies are applied to prevent congestion before it happens. The congestion control is handled either by the source or the destination.
Closed-loop congestion control technique is used to treat or alleviate congestion after it happens.
Total length field and header checksum of IPv4 header change from router to router.
40.The value of HLEN in an IPv4 datagram is 7.How many option bytes are present?
If the value of the HLEN field is 7 , then there are 28 (since 7 × 4 = 28) bytes included in the header.
The value of the header length field of an IP packet can never be less than 5 because every IP datagram must have at least a base header that has a fixed size of 20 bytes.
if a source is sending 100 datagrams and for the first datagram identification no is 1024 then for the last datagram identification number will be 1024 + 99 = 1123.
The checksum is eliminated in IPv6 because it is provided by upper-layer protocols; it is therefore not needed at this level.
A technique of internetworking called Tunneling is used when the source and destination networks of the same type are to be connected through a network of a different type.
The first 4-bits show version i.e. 0100 which belongs to IP version 4.
Fragmentation is an important function of the network layer. It is a technique in which gateways break up or divide larger packets into smaller ones called fragments. Each fragment is then sent as a separate internal packet. Each fragment has its own separate header and trailer. Sometimes, a fragmented datagram also gets fragmented when it encounters a network that handles smaller fragments. Thus, a datagram can be fragmented several times before it reaches its final destination. The reverse process of fragmentation is difficult. Reassembly of fragments is usually done by the destination host because each fragment has become an independent datagram.
Transmission Speed = 10Mbps.
Round trip propagation delay = 46.4 ms
The minimum frame size = (Round Trip Propagation Delay) * (Transmission Speed) = 10*(10^6)*46.4*(10^-3) = 464 * 10^3 = 464 Kbit
In the slow start phase of the TCP congestion control algorithm, the size of the congestion window increases exponentially.
The maximum window size for data transmission using the Selective Reject protocol with the n-bit frame sequence number is [Tex]2^(n-1) [/Tex] .
As you study these top 50 TCP/IP interview questions and answers, remember to not only memorize the answers but also to understand the basic principles. Whether you are just starting your career or looking to advance, this questions will serve as a strong foundation for your professional growth in the ever-evolving world of networking. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your skills and stand out to potential employers.